Reference: Digital Image Processing from Prof. Ghassan Alregib
Analog vs. Digital


Why 'Rectangular' Lattice/Sampling?
- m = horizontal sampling intervals of period (X, 2X, 3X, ...)
- n = vertical sampling intervals of period (Y, 2Y, 3Y, ...)
- Here, X and Y refers to the sampling interval in the x/y direction each.
- Rectangular sampling is defined by the periodicity of the sampling interval in the x/y direction.
- pi, omega is two frequencies?
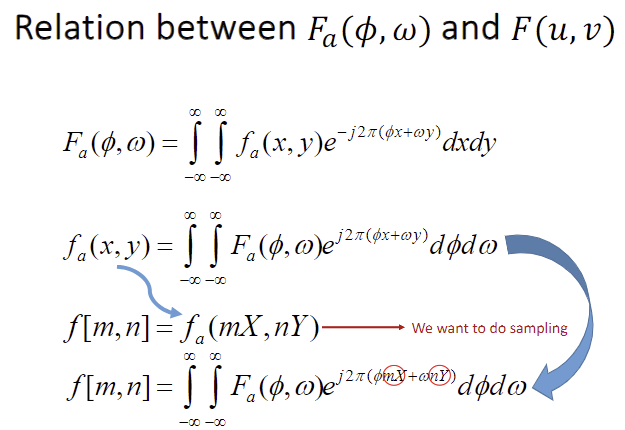
- m,n is an integer, finite values. -> f[m,n] shall be sampling.
- Fourier transform(F(u,v)), however, is continuous in terms of u and v.


- The right image is sampled image of the left image.
- Low rate of sampling: Still maintain the structure & details of the image.


- Below are the definitions of the fourier transform in analog signal.
- image in (6,4) coordinate would be similar to f_a(12,12).

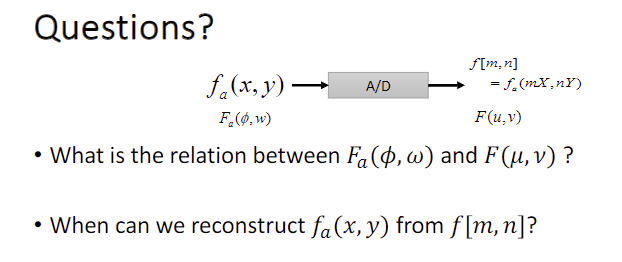
- What is the relation between the fourier transform of our continuous signal / digital signal?
- When can we reconstruct our analog signal from digital signal, covered by the sampling theorem?



- Here, X and Y are scaling factors.
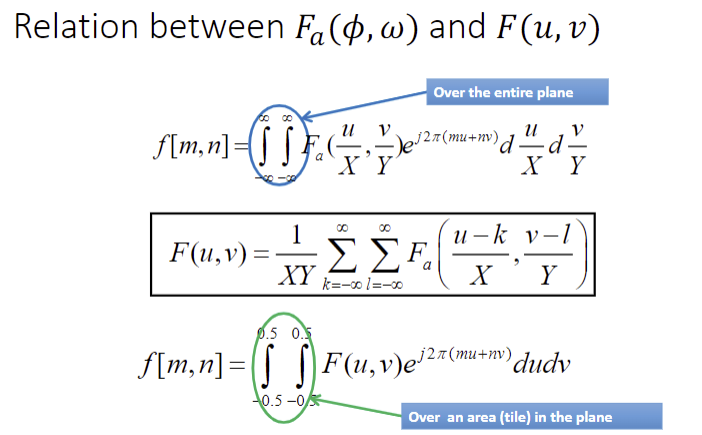

- F_a and F shall be similar, just scaling matters.

- right image: spatial domain (circle repeated)
- bandlimited study: choice of X and Y can interfere the other circle(or maybe W).
- In order not to interfere, the maximum frequency X <= 1/W


'Georgia Institute of Technology > Digital Signal Processing' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Interpolation (0) | 2023.09.12 |
|---|---|
| Frequency Response & DTFT (0) | 2023.09.11 |
| 2D Convolution (0) | 2023.09.06 |
| Multidimensional Signal Processing (0) | 2023.09.05 |
| Image Sensors (1) | 2023.08.23 |




댓글