출처 : (4) 3D Computer Vision | Lecture 6 (Part 2): Single view metrology - YouTube
Objective
- Compute the Homography Matrix which can map the image quadrilateral to a rectangle with the correct aspect ratio.
- Map the Source image to the Target image using the homography matrix.

- Implement Planar Mosaicing: Images acquired by a camera rotating about its center are related by a planar homography.
- For example, we could stitch the below 3 images to make the panoramic view.

- In outline, the algorithm is:
- Choose one image as a reference.
- Compute the homography matrix which maps one of the other images to the reference image.
- Wrap the image with this homography (here, Augment the reference image with the non-overlapping part of the wrapped image).
- Repeat the last two steps for the remaining images.
- Note that the homography matrix could be only computed in the two images which share the overlapping view.
- Homography(3->5) = Homography(3->4) x Homography(3->5)
What does Calibration Give?
- Suppose Points on the ray are written as X = (x, y, z) in the camera Euclidean coordinate frame.
- Then these points map to the point x as below.
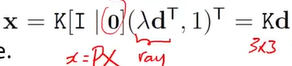
- In other words, we can obtain the direction d by given intrinsic parameter K.
- Furthermore, we can obtain the angle between two rays as below.

- In other words, the calibrated camera could be used like a direction sensor like a 2D protractor.
The Image of the Absolute Conic
- The absolute conic is defined in the plane of infinity.
- By knowing the intrinsic value,
'Computer Vision > Multiple View Geometry' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Multiple View Geometry] RANSAC (0) | 2023.03.12 |
|---|---|
| [Multiple View Geometry] Iterative minimization (반복최소화 방법) (0) | 2023.03.12 |
| [Multiple View Geometry] 이미지에서 아핀변환과 거리 속성의 복원 (0) | 2022.10.02 |
| Epipolar Geometry (0) | 2022.08.28 |
| [Multiple View Geometry] Conics, Quadrics (0) | 2022.08.28 |




댓글